Subtitles, Captions, or Dubbing: Video Localization Guide
Last Updated

AI Video Translator, Localization, and Dubbing Tool
Try it out for Free
Jump to section
Jump to section
Share
Share
Share
When you start localizing video content, one question comes up very quickly.
Should you use subtitles, captions, or dubbing?
Each option solves a different problem. Each one fits a different type of video.
And choosing the wrong method can hurt clarity, engagement, or budget.
This guide is here to help you decide. We will look at how subtitles, captions, and dubbing differ, when each option works best, and how they fit into a broader video localization strategy.
Subtitles, Captions, and Dubbing: What’s the Difference?
Before choosing a method, it helps to understand what each one is meant to do. This section keeps it simple and practical.
Subtitles Brief definition focused on purpose, not history.
Subtitles are on-screen text that translates spoken dialogue into another language.
They are mainly designed for non-native speakers who want to understand the original video without changing the audio.
Subtitles focus on meaning, not sound details. They translate what is said, but usually do not include music cues or background noise. This makes them a common and cost-effective way to localize video for international audiences.
Captions Accessibility-focused explanation only.
Captions are also on-screen text, but their purpose is different.
They are designed for accessibility.
Captions include dialogue as well as non-speech elements like music, sound effects, or tone indicators. This helps viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing follow both the story and the context of the video.
Because of this, captions are often required for compliance and are widely used across platforms where accessibility matters.
Dubbing High-level explanation without going into AI or workflow depth.
Dubbing replaces the original audio with a voice track in the target language.
Instead of reading text, viewers hear the content spoken in their own language.
The goal of dubbing is immersion. When done well, it allows viewers to focus entirely on the visuals and story, without on-screen text. Dubbing is commonly used for entertainment, marketing, and high-impact video content.
When Subtitles Are the Best Choice
Subtitles for Educational and Informational Videos
Subtitles are an excellent choice for elearning, training videos, and product demos. They allow viewers to follow along with the audio while reading the translation in their own language, improving understanding and knowledge retention. This makes video content more impactful.
Subtitles for Fast and Cost-Effective Localization
Here are a few benefits of using subtitles. They are:
Best for educational, training, and product demo videos
Working well when viewers are comfortable reading on-screen text
Faster to produce than dubbing for multi-language distribution
Easier to update when scripts or terminology change
Suitable when preserving the original speaker’s voice matters
Limitations of Subtitles
While subtitles are cost-effective, they have limitations. Some viewers find reading subtitles distracting or prefer not to read. Also, text expansion can be an issue, where translated text requires more space than the original, potentially covering important visuals in the original video. Consider these factors when deciding if subtitles are the right way to localize.
In practice, subtitles are best suited for content where speed, clarity, and multilingual scalability are more important than full audio immersion.
When Captions Make More Sense
Captions for Accessibility and Compliance
Captions are essential for making video content accessible to viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing. By providing a text version of the audio and video, including dialogue and non-speech elements like music, captions ensure inclusivity. This is not only a best practice but often a legal requirement for compliance, enhancing accessibility to localize your video.
Captions for Silent Viewing and Social Media
In today's mobile-first world, many people watch videos on mute, especially on social media platforms. Captions allow viewers to understand the video content without needing the audio and video, increasing engagement and reach. If you want a cost-effective way to create content accessible, captions are the smart move for your global content.
Where Captions Fall Short
While captions excel at accessibility, they may not be ideal for all video localization needs. For viewers who aren't hard of hearing but don't speak the original language, subtitles might be a better option. Additionally, captions don't address the native language preferences as comprehensively as dubbing or subtitles.
Captions are most effective when accessibility, compliance, or silent viewing conditions are the primary considerations.
When Dubbing Is the Better Option
Dubbing for Immersive Viewer Experience
Dubbing provides an immersive viewing experience by replacing the original audio with voiceovers in the target language
It eliminates the need for viewers to read on-screen text, allowing full focus on the visuals and story
Dubbing is a way to localize video content that feels natural and engaging for the audience
Dubbing for Marketing and Entertainment Content
For marketing and entertainment content, dubbing can be particularly effective.
By delivering the message in the viewer’s native language, dubbing helps create a stronger emotional connection
It supports cultural resonance, making the content feel more relevant to local audiences
This approach ensures the video message truly localizes when reaching new audiences
Trade-offs of Using Dubbing
While dubbing offers a better viewing experience, it typically requires more resources and time compared to subtitles. The process involves professional voice-over artists and careful synchronization to match lip movements. Despite this, advancements in AI dubbing are rapidly making dubbing solutions more cost-efficient.
Dubbing is typically chosen when viewer immersion and emotional impact are prioritized over production simplicity.
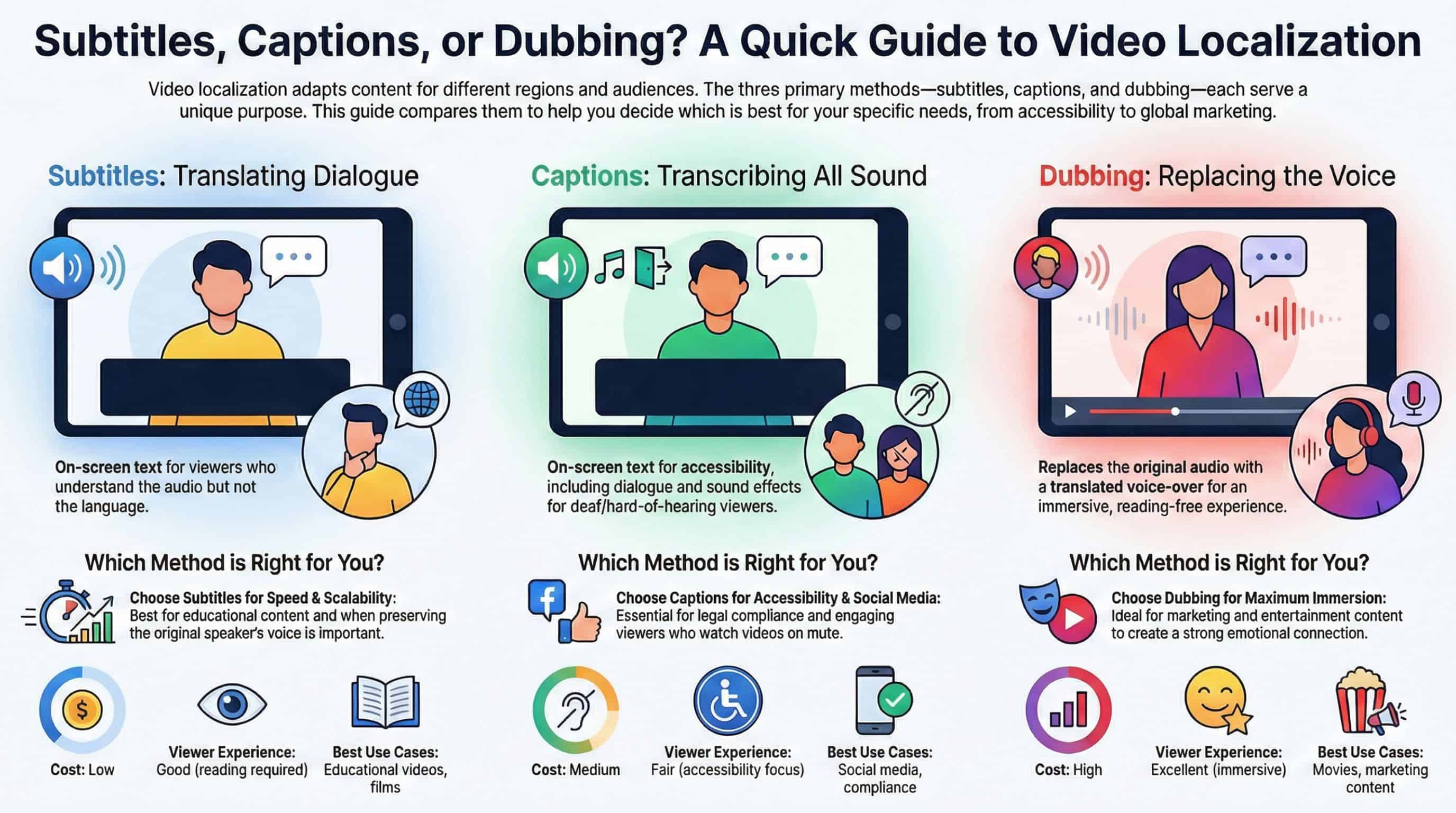
Subtitles vs Captions vs Dubbing: Side-by-Side Comparison
Cost and Production Effort
Subtitles are the most cost-effective, followed by captions. Dubbing, especially traditional dubbing, typically involves higher production costs and more effort. However, AI tools are helping to reduce the cost of dubbing, making it more affordable for single video projects.
Viewer Experience and Engagement
Dubbing generally offers the most immersive viewing experience, as it eliminates the need to read. Subtitles provide a balance between cost and engagement, while captions focus primarily on accessibility. The best option depends on the video content and native language preference of the new audiences.
Scalability Across Languages
Different methods exist to adapt video content for diverse audiences. Subtitles offer a cost-effective solution with fast production times, providing a good viewer experience for non-native speakers. Captions balance accessibility with moderate production time and cost. Dubbing delivers an immersive experience but is the most expensive and time-consuming option.
Feature | Subtitles | Captions | Dubbing |
Cost | Low | Medium | High |
Production Time | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
Viewer Experience | Good (reading required) | Fair (accessibility focus) | Excellent (immersive) |
Accessibility | Good (for non-native speakers) | Excellent (for deaf/hard of hearing) | Good (if well-synced) |
Scalability | High (easy to translate into many languages) | High (easy to transcribe and translate) | Moderate (requires voiceovers for each language) |
Use Cases | Educational videos, films | Social media, compliance | Movies, marketing content |
Translation quality | High translation accuracy with AI | Accurate transcription and translation | Depends on voice-over and AI sync |
Impact | Broad reach among non-native speakers | Inclusive for all viewers | High emotional connection |
ROI | High if done well | Medium | Potentially high depending on content quality |
How to Choose the Right Localization Method
Content Type and Video Format
The type of video content and its format significantly influence the choice between subtitles, captions, and dubbing. For instance, elearning and training videos benefit greatly from subtitles due to their cost-effective nature and ability to aid comprehension of information in their native language. In contrast, short-form video content on social media often thrives with captions due to silent viewing habits.
Audience Expectations and Language Preferences
Understanding your new audiences' expectations and native language preferences is paramount. In some cultures, dubbing is preferred for entertainment content, while others may appreciate the authenticity of original language with subtitles. Polling your audience or researching regional preferences ensures your video localization strategy aligns with their needs, maximizing engagement and ROI.
Budget, Timeline, and Distribution Channels
Budget, timeline, and distribution channels are critical factors. Subtitles are generally the most cost-effective to localize, making them suitable for projects with limited resources. Dubbing, while offering a better viewing experience, demands a more significant investment. AI dubbing is changing this, making dubbing solutions more accessible for single video projects with tighter budgets and shorter timelines, allowing for rapid translation.
How These Methods Fit into a Video Localization Strategy
Combining Subtitles, Captions, and Dubbing
A comprehensive video localization strategy might involve combining subtitles, captions, and dubbing for different segments of your audience. For instance, you could offer dubbing in key markets while providing subtitles in other languages to cater to diverse preferences. Captions should be a standard inclusion for accessibility, ensuring inclusivity across all video files.
Scaling Video Localization Over Time
As your global content needs grow, consider a scalable video localization approach. Start with subtitles in the most critical target language and gradually introduce dubbing as resources permit. Leverage translation tools and AI video solutions to streamline the process and reduce costs. Tools that transcribe and translate video can help with your content creation.
Key Takeaways
Choosing between subtitles, captions, and dubbing depends on the type of content, the needs of the audience, and how the video will be distributed. Subtitles are often used for speed and multilingual reach, captions support accessibility and silent viewing, and dubbing prioritizes immersion and emotional impact. In practice, video localization strategies frequently combine these methods and evolve over time as content libraries and audience expectations change.
When you start localizing video content, one question comes up very quickly.
Should you use subtitles, captions, or dubbing?
Each option solves a different problem. Each one fits a different type of video.
And choosing the wrong method can hurt clarity, engagement, or budget.
This guide is here to help you decide. We will look at how subtitles, captions, and dubbing differ, when each option works best, and how they fit into a broader video localization strategy.
Subtitles, Captions, and Dubbing: What’s the Difference?
Before choosing a method, it helps to understand what each one is meant to do. This section keeps it simple and practical.
Subtitles Brief definition focused on purpose, not history.
Subtitles are on-screen text that translates spoken dialogue into another language.
They are mainly designed for non-native speakers who want to understand the original video without changing the audio.
Subtitles focus on meaning, not sound details. They translate what is said, but usually do not include music cues or background noise. This makes them a common and cost-effective way to localize video for international audiences.
Captions Accessibility-focused explanation only.
Captions are also on-screen text, but their purpose is different.
They are designed for accessibility.
Captions include dialogue as well as non-speech elements like music, sound effects, or tone indicators. This helps viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing follow both the story and the context of the video.
Because of this, captions are often required for compliance and are widely used across platforms where accessibility matters.
Dubbing High-level explanation without going into AI or workflow depth.
Dubbing replaces the original audio with a voice track in the target language.
Instead of reading text, viewers hear the content spoken in their own language.
The goal of dubbing is immersion. When done well, it allows viewers to focus entirely on the visuals and story, without on-screen text. Dubbing is commonly used for entertainment, marketing, and high-impact video content.
When Subtitles Are the Best Choice
Subtitles for Educational and Informational Videos
Subtitles are an excellent choice for elearning, training videos, and product demos. They allow viewers to follow along with the audio while reading the translation in their own language, improving understanding and knowledge retention. This makes video content more impactful.
Subtitles for Fast and Cost-Effective Localization
Here are a few benefits of using subtitles. They are:
Best for educational, training, and product demo videos
Working well when viewers are comfortable reading on-screen text
Faster to produce than dubbing for multi-language distribution
Easier to update when scripts or terminology change
Suitable when preserving the original speaker’s voice matters
Limitations of Subtitles
While subtitles are cost-effective, they have limitations. Some viewers find reading subtitles distracting or prefer not to read. Also, text expansion can be an issue, where translated text requires more space than the original, potentially covering important visuals in the original video. Consider these factors when deciding if subtitles are the right way to localize.
In practice, subtitles are best suited for content where speed, clarity, and multilingual scalability are more important than full audio immersion.
When Captions Make More Sense
Captions for Accessibility and Compliance
Captions are essential for making video content accessible to viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing. By providing a text version of the audio and video, including dialogue and non-speech elements like music, captions ensure inclusivity. This is not only a best practice but often a legal requirement for compliance, enhancing accessibility to localize your video.
Captions for Silent Viewing and Social Media
In today's mobile-first world, many people watch videos on mute, especially on social media platforms. Captions allow viewers to understand the video content without needing the audio and video, increasing engagement and reach. If you want a cost-effective way to create content accessible, captions are the smart move for your global content.
Where Captions Fall Short
While captions excel at accessibility, they may not be ideal for all video localization needs. For viewers who aren't hard of hearing but don't speak the original language, subtitles might be a better option. Additionally, captions don't address the native language preferences as comprehensively as dubbing or subtitles.
Captions are most effective when accessibility, compliance, or silent viewing conditions are the primary considerations.
When Dubbing Is the Better Option
Dubbing for Immersive Viewer Experience
Dubbing provides an immersive viewing experience by replacing the original audio with voiceovers in the target language
It eliminates the need for viewers to read on-screen text, allowing full focus on the visuals and story
Dubbing is a way to localize video content that feels natural and engaging for the audience
Dubbing for Marketing and Entertainment Content
For marketing and entertainment content, dubbing can be particularly effective.
By delivering the message in the viewer’s native language, dubbing helps create a stronger emotional connection
It supports cultural resonance, making the content feel more relevant to local audiences
This approach ensures the video message truly localizes when reaching new audiences
Trade-offs of Using Dubbing
While dubbing offers a better viewing experience, it typically requires more resources and time compared to subtitles. The process involves professional voice-over artists and careful synchronization to match lip movements. Despite this, advancements in AI dubbing are rapidly making dubbing solutions more cost-efficient.
Dubbing is typically chosen when viewer immersion and emotional impact are prioritized over production simplicity.

Subtitles vs Captions vs Dubbing: Side-by-Side Comparison
Cost and Production Effort
Subtitles are the most cost-effective, followed by captions. Dubbing, especially traditional dubbing, typically involves higher production costs and more effort. However, AI tools are helping to reduce the cost of dubbing, making it more affordable for single video projects.
Viewer Experience and Engagement
Dubbing generally offers the most immersive viewing experience, as it eliminates the need to read. Subtitles provide a balance between cost and engagement, while captions focus primarily on accessibility. The best option depends on the video content and native language preference of the new audiences.
Scalability Across Languages
Different methods exist to adapt video content for diverse audiences. Subtitles offer a cost-effective solution with fast production times, providing a good viewer experience for non-native speakers. Captions balance accessibility with moderate production time and cost. Dubbing delivers an immersive experience but is the most expensive and time-consuming option.
Feature | Subtitles | Captions | Dubbing |
Cost | Low | Medium | High |
Production Time | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
Viewer Experience | Good (reading required) | Fair (accessibility focus) | Excellent (immersive) |
Accessibility | Good (for non-native speakers) | Excellent (for deaf/hard of hearing) | Good (if well-synced) |
Scalability | High (easy to translate into many languages) | High (easy to transcribe and translate) | Moderate (requires voiceovers for each language) |
Use Cases | Educational videos, films | Social media, compliance | Movies, marketing content |
Translation quality | High translation accuracy with AI | Accurate transcription and translation | Depends on voice-over and AI sync |
Impact | Broad reach among non-native speakers | Inclusive for all viewers | High emotional connection |
ROI | High if done well | Medium | Potentially high depending on content quality |
How to Choose the Right Localization Method
Content Type and Video Format
The type of video content and its format significantly influence the choice between subtitles, captions, and dubbing. For instance, elearning and training videos benefit greatly from subtitles due to their cost-effective nature and ability to aid comprehension of information in their native language. In contrast, short-form video content on social media often thrives with captions due to silent viewing habits.
Audience Expectations and Language Preferences
Understanding your new audiences' expectations and native language preferences is paramount. In some cultures, dubbing is preferred for entertainment content, while others may appreciate the authenticity of original language with subtitles. Polling your audience or researching regional preferences ensures your video localization strategy aligns with their needs, maximizing engagement and ROI.
Budget, Timeline, and Distribution Channels
Budget, timeline, and distribution channels are critical factors. Subtitles are generally the most cost-effective to localize, making them suitable for projects with limited resources. Dubbing, while offering a better viewing experience, demands a more significant investment. AI dubbing is changing this, making dubbing solutions more accessible for single video projects with tighter budgets and shorter timelines, allowing for rapid translation.
How These Methods Fit into a Video Localization Strategy
Combining Subtitles, Captions, and Dubbing
A comprehensive video localization strategy might involve combining subtitles, captions, and dubbing for different segments of your audience. For instance, you could offer dubbing in key markets while providing subtitles in other languages to cater to diverse preferences. Captions should be a standard inclusion for accessibility, ensuring inclusivity across all video files.
Scaling Video Localization Over Time
As your global content needs grow, consider a scalable video localization approach. Start with subtitles in the most critical target language and gradually introduce dubbing as resources permit. Leverage translation tools and AI video solutions to streamline the process and reduce costs. Tools that transcribe and translate video can help with your content creation.
Key Takeaways
Choosing between subtitles, captions, and dubbing depends on the type of content, the needs of the audience, and how the video will be distributed. Subtitles are often used for speed and multilingual reach, captions support accessibility and silent viewing, and dubbing prioritizes immersion and emotional impact. In practice, video localization strategies frequently combine these methods and evolve over time as content libraries and audience expectations change.
Continue Reading
Browse All
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618





