
✨New
Get All Key Features for Just $6.99
Video Localization: A Practical Guide to Video Translation
Last Updated
January 16, 2026

AI Video Translator, Localization, and Dubbing Tool
Try it out for Free
Jump to section
Jump to section
Share
Share
Share
Video content is everywhere. People watch videos to learn, buy, and make decisions. But if your audience speaks a different language, your message can break fast.
That’s where video localization becomes essential.
It is not just language translation. It is the process of adapting video content so it feels natural in new languages and regions. That includes the audio and video, on-screen text, and even cultural context.
If your message feels “foreign”, your audience will scroll. If it feels native, they stay.
Understanding Video Localization
What is Video Localization?
Video localization is the process of taking an original video and making it work for a new target language and audience.
This goes beyond simple translation. You may need to adapt the video script, on-screen text (titles, labels, UI), subtitles or dubbing, voice in the target language, cultural references (tone, examples, idioms).
If you are using an ai video translator, you can move faster. But you still need a clear workflow so quality does not drop. A good AI-powered video localization platform may help you keep high quality standard.
The Importance of Video Localization
If your video needs global reach, you cannot rely on one language.
When people get information in their native language, they trust it more. They also understand instructions faster, especially in an instructional video.
So the goal is simple - to reduce confusion, increase watch time, improve conversions, and support accessibility.
Key Components of Video Localization
A successful video localization setup usually includes:
Script work: translation and localization, not word-for-word
Subtitles/captions: timing, readability, and clarity
Voice options: voiceovers or dubbing
Visual updates: adapting text inside graphics
QA: checking pacing, tone, and meaning
When localizing video content, small details matter. Especially names, numbers, and calls to action.
Video Translation and Localization Services
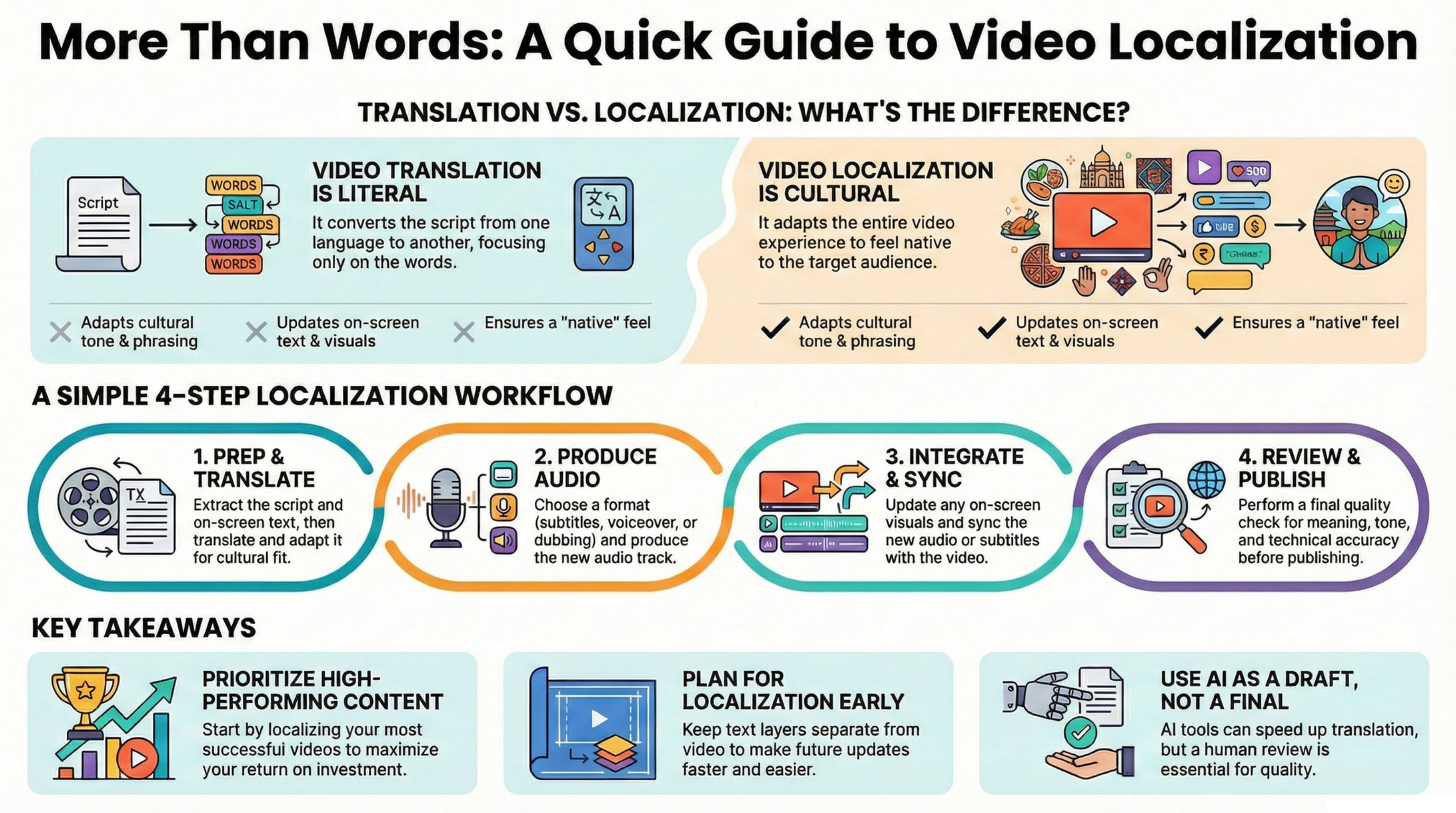
Overview of Translation and Localization Services
Video translation and localization services help you scale one video into many markets.
A language service may include:
translating the script of the english video
creating subtitles
recording voice-over
full dubbing
on-screen text editing
If you only translate, the original video can still feel “off” to viewers. That is why localization experts and localization professionals usually recommend adapting more than just words.
Comparison of Video Translation and Localization
Here’s the clean way to think about it:
Task | Video translation | Video localization |
Converts text to a new language | Yes | Yes |
Adapts tone and phrasing | Sometimes | Yes |
Updates visuals and on-screen text | No | Often |
Handles cultural fit | No | Yes |
Supports immersive formats | Limited | Strong |
Video translation and localization are related, but not equal. One is literal. The other is designed for real people in real markets.
Choosing the Right Localization Service
Pick based on your goal and budget. If it’s a single video for internal training, subtitles may be enough. If it’s customer-facing marketing, you may want dubbing or a voice-over that matches the original audio style.
A good way to localize video is to start small. Pick 1-2 languages Localize the highest-performing content first. Then scale once your workflow is stable.
Best Practices for Video Localization
Video Localization Best Practices
These video localization best practices keep quality high while staying efficient:
Plan localization early in video production
Keep text layers separate (avoid hard-baked subtitles)
Leave room for text expansion
Build a glossary for consistent terms
Always review the localized output before publishing
This is how you avoid mistakes that make your brand look sloppy.
Methods of Video Localization
There are different methods of video localization. The best option depends on format, audience, and channel. Common video localization methods include subtitles, captions, voice-over, dubbing, replacing on-screen text. Most teams combine methods of video localization. Example: subtitles for long-form education, dubbing for ads and entertainment.
AI is now part of most workflows. ai video tools can help with: speech-to-text, automated translation, subtitle timing, voice generation.
AI dubbing can be a cost-effective way to scale. But do not skip review. AI can miss meaning, tone, and cultural nuance. So the best workflow is AI speed + human accuracy.
AI can draft. Humans decide.
Benefits of Video Localization
Why Localizing Video Content Matters
Localizing video content helps make information more accessible to viewers who may not speak the original language. By adapting language, audio, and visuals, videos can communicate ideas more clearly and reduce misunderstandings across regions.
This approach is particularly useful for instructional, educational, and informational videos where clarity is essential. Localization also supports inclusivity by making content easier to follow for audiences with different language preferences.
Impact on Global Reach
When you localize your video content, you unlock a global video strategy.
You can repurpose the same idea into multiple markets. This also supports brand consistency, because you control how your message is presented.
One more key point: without localization, even great content can underperform internationally. The message is there, but the audience does not feel it.
Enhancing Audience Engagement through Localization
Engagement grows when the experience feels native.
If the original english in the video is replaced with natural localized delivery, people stay longer. They also take action more often.
This is why brands invest in localization even when they already have subtitles.
The Video Localization Process
Steps in the Localization Process
Here is a clean localization process you can reuse for every project:
Review the original video and define voice translator needs
Extract the script, including any on-screen text
Translate and adapt for the target language
Choose format: subtitles, voiceover, or dubbing
Produce audio, sync timing, and update visuals
QA review (meaning, tone, and cultural fit)
Upload your video and publish
This is the process of adapting video content in a way that scales.
Video Script Translation and Adaptation
This step is where most quality is won or lost.
Your video script must sound like a real person in the new market, not a translated document. That often means rephrasing, shortening, or changing examples.
Also double-check any script of the english video that includes jokes, slang, or local cultural references.
Subtitles are fast and flexible. Voiceovers feel more personal. Dubbing is the most immersive, and similar to dubbing in film and TV.
A simple rule to keep in mind is to use Subtitles for speed and accessibility, Voice-over for learning and explainers, and Dubbing for marketing and entertainment.
Multimedia Localization and Its Role
Understanding Multimedia Localization
Multimedia localization covers more than dialogue. It includes anything the viewer sees and hears.
That means graphics, UI elements, labels, and calls to action. It connects the whole audio and video experience.
Challenges in Multimedia Localization
Typical issues include:
timing constraints
text expansion
lip-sync and pacing
formatting differences
cultural mismatches in visuals
This is why teams often use specialized workflows and tools, not generic translation alone.
Integrating Multimedia Localization into Your Strategy
Treat localization like a system, not a one-off task.
Build templates, reuse glossaries, and keep your assets organized. Over time, localizing video content becomes faster and more predictable.
A smart way to localize video at scale is to start with your best-performing videos, then expand into more languages.
Key Takeaways
Video localization is the process of adapting a video for new markets, not just translating words. The best results come from combining translation + cultural fit + format choices (subtitles, voiceover, dubbing). Good AI software helps you scale faster, but review protects quality.
Video content is everywhere. People watch videos to learn, buy, and make decisions. But if your audience speaks a different language, your message can break fast.
That’s where video localization becomes essential.
It is not just language translation. It is the process of adapting video content so it feels natural in new languages and regions. That includes the audio and video, on-screen text, and even cultural context.
If your message feels “foreign”, your audience will scroll. If it feels native, they stay.
Understanding Video Localization
What is Video Localization?
Video localization is the process of taking an original video and making it work for a new target language and audience.
This goes beyond simple translation. You may need to adapt the video script, on-screen text (titles, labels, UI), subtitles or dubbing, voice in the target language, cultural references (tone, examples, idioms).
If you are using an ai video translator, you can move faster. But you still need a clear workflow so quality does not drop. A good AI-powered video localization platform may help you keep high quality standard.
The Importance of Video Localization
If your video needs global reach, you cannot rely on one language.
When people get information in their native language, they trust it more. They also understand instructions faster, especially in an instructional video.
So the goal is simple - to reduce confusion, increase watch time, improve conversions, and support accessibility.
Key Components of Video Localization
A successful video localization setup usually includes:
Script work: translation and localization, not word-for-word
Subtitles/captions: timing, readability, and clarity
Voice options: voiceovers or dubbing
Visual updates: adapting text inside graphics
QA: checking pacing, tone, and meaning
When localizing video content, small details matter. Especially names, numbers, and calls to action.
Video Translation and Localization Services

Overview of Translation and Localization Services
Video translation and localization services help you scale one video into many markets.
A language service may include:
translating the script of the english video
creating subtitles
recording voice-over
full dubbing
on-screen text editing
If you only translate, the original video can still feel “off” to viewers. That is why localization experts and localization professionals usually recommend adapting more than just words.
Comparison of Video Translation and Localization
Here’s the clean way to think about it:
Task | Video translation | Video localization |
Converts text to a new language | Yes | Yes |
Adapts tone and phrasing | Sometimes | Yes |
Updates visuals and on-screen text | No | Often |
Handles cultural fit | No | Yes |
Supports immersive formats | Limited | Strong |
Video translation and localization are related, but not equal. One is literal. The other is designed for real people in real markets.
Choosing the Right Localization Service
Pick based on your goal and budget. If it’s a single video for internal training, subtitles may be enough. If it’s customer-facing marketing, you may want dubbing or a voice-over that matches the original audio style.
A good way to localize video is to start small. Pick 1-2 languages Localize the highest-performing content first. Then scale once your workflow is stable.
Best Practices for Video Localization
Video Localization Best Practices
These video localization best practices keep quality high while staying efficient:
Plan localization early in video production
Keep text layers separate (avoid hard-baked subtitles)
Leave room for text expansion
Build a glossary for consistent terms
Always review the localized output before publishing
This is how you avoid mistakes that make your brand look sloppy.
Methods of Video Localization
There are different methods of video localization. The best option depends on format, audience, and channel. Common video localization methods include subtitles, captions, voice-over, dubbing, replacing on-screen text. Most teams combine methods of video localization. Example: subtitles for long-form education, dubbing for ads and entertainment.
AI is now part of most workflows. ai video tools can help with: speech-to-text, automated translation, subtitle timing, voice generation.
AI dubbing can be a cost-effective way to scale. But do not skip review. AI can miss meaning, tone, and cultural nuance. So the best workflow is AI speed + human accuracy.
AI can draft. Humans decide.
Benefits of Video Localization
Why Localizing Video Content Matters
Localizing video content helps make information more accessible to viewers who may not speak the original language. By adapting language, audio, and visuals, videos can communicate ideas more clearly and reduce misunderstandings across regions.
This approach is particularly useful for instructional, educational, and informational videos where clarity is essential. Localization also supports inclusivity by making content easier to follow for audiences with different language preferences.
Impact on Global Reach
When you localize your video content, you unlock a global video strategy.
You can repurpose the same idea into multiple markets. This also supports brand consistency, because you control how your message is presented.
One more key point: without localization, even great content can underperform internationally. The message is there, but the audience does not feel it.
Enhancing Audience Engagement through Localization
Engagement grows when the experience feels native.
If the original english in the video is replaced with natural localized delivery, people stay longer. They also take action more often.
This is why brands invest in localization even when they already have subtitles.
The Video Localization Process
Steps in the Localization Process
Here is a clean localization process you can reuse for every project:
Review the original video and define voice translator needs
Extract the script, including any on-screen text
Translate and adapt for the target language
Choose format: subtitles, voiceover, or dubbing
Produce audio, sync timing, and update visuals
QA review (meaning, tone, and cultural fit)
Upload your video and publish
This is the process of adapting video content in a way that scales.
Video Script Translation and Adaptation
This step is where most quality is won or lost.
Your video script must sound like a real person in the new market, not a translated document. That often means rephrasing, shortening, or changing examples.
Also double-check any script of the english video that includes jokes, slang, or local cultural references.
Subtitles are fast and flexible. Voiceovers feel more personal. Dubbing is the most immersive, and similar to dubbing in film and TV.
A simple rule to keep in mind is to use Subtitles for speed and accessibility, Voice-over for learning and explainers, and Dubbing for marketing and entertainment.
Multimedia Localization and Its Role
Understanding Multimedia Localization
Multimedia localization covers more than dialogue. It includes anything the viewer sees and hears.
That means graphics, UI elements, labels, and calls to action. It connects the whole audio and video experience.
Challenges in Multimedia Localization
Typical issues include:
timing constraints
text expansion
lip-sync and pacing
formatting differences
cultural mismatches in visuals
This is why teams often use specialized workflows and tools, not generic translation alone.
Integrating Multimedia Localization into Your Strategy
Treat localization like a system, not a one-off task.
Build templates, reuse glossaries, and keep your assets organized. Over time, localizing video content becomes faster and more predictable.
A smart way to localize video at scale is to start with your best-performing videos, then expand into more languages.
Key Takeaways
Video localization is the process of adapting a video for new markets, not just translating words. The best results come from combining translation + cultural fit + format choices (subtitles, voiceover, dubbing). Good AI software helps you scale faster, but review protects quality.
Continue Reading
Browse All
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618
PRODUCT
USE CASE
ESTsoft Inc. 15770 Laguna Canyon Rd #250, Irvine, CA 92618





